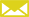
A cold storage evaporator plays a crucial role in maintaining low temperatures within the storage environment through the process of heat exchange and refrigeration cycle. The evaporator is a heat exchanger located within the cold storage space, typically in close proximity to the stored items.
Here's how the cold storage evaporator contributes to temperature control:
Heat Absorption: The evaporator contains a refrigerant that enters as a low-pressure, low-temperature liquid. As the warm air from the storage space is drawn over the evaporator coils, the refrigerant inside the coils absorbs the heat from the air. This heat absorption causes the refrigerant to evaporate and transform into a low-pressure gas.
Temperature Reduction: As the refrigerant absorbs heat from the surrounding air, the air's temperature decreases. This cooled air is then circulated back into the storage area, effectively reducing the temperature within the storage space.


Continuous Cycle: The evaporated refrigerant gas is then sent to the compressor, where it's compressed, raising its temperature and pressure. This high-pressure, high-temperature gas is then directed to the condenser coils located outside the cold storage area.
Heat Rejection: In the condenser, the refrigerant releases the heat it absorbed from the storage area to the outside environment. This causes the refrigerant to condense back into a liquid state.
Refrigerant Recovery: The condensed refrigerant liquid then flows through an expansion valve, which reduces its pressure and temperature, preparing it to enter the evaporator once again.
By continuously cycling the refrigerant through this process, the cold storage evaporator consistently removes heat from the storage area and releases it outside, allowing the temperature within the storage space to remain at the desired low level. The evaporator effectively acts as a cooling mechanism, ensuring that the stored items are kept at the specified temperature to prevent spoilage, maintain product quality, and extend shelf life.